Database Record Viewer Horse Side Vet Guide
The horse's general form is characteristic of an animal of speed: the long leg bones pivot on pulley-like joints that restrict movement to the fore and aft, the limbs are levered to muscle masses in such a way as to provide the most efficient use of energy, and the compact body is supported permanently on the tips of the toes, allowing fuller ex.

Running Horse in the Desert Stock Photo Image of galloping, nature 18709594
Neck: The portion of the horse's body that is between the head and shoulders. Shoulder: The upper portion of the horse's front leg. Withers: The bony ridge at the base of the neck between the shoulder blades. This ridge is created by the top portion of the thoracic vertebrae. Horses are measured at the withers.
Horse Anatomy Reference Vitals & Anatomy upyourbutthealing
An abnormality in a horse's movement caused by pain or reduced range of motion. It is commonly used interchangeably with the term unsoundness since a "sound" horse is one that is not lame. Lameness or Unsoundness
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stockings-58d91d713df78c5162d10342.jpg)
White Leg Markings on Horses
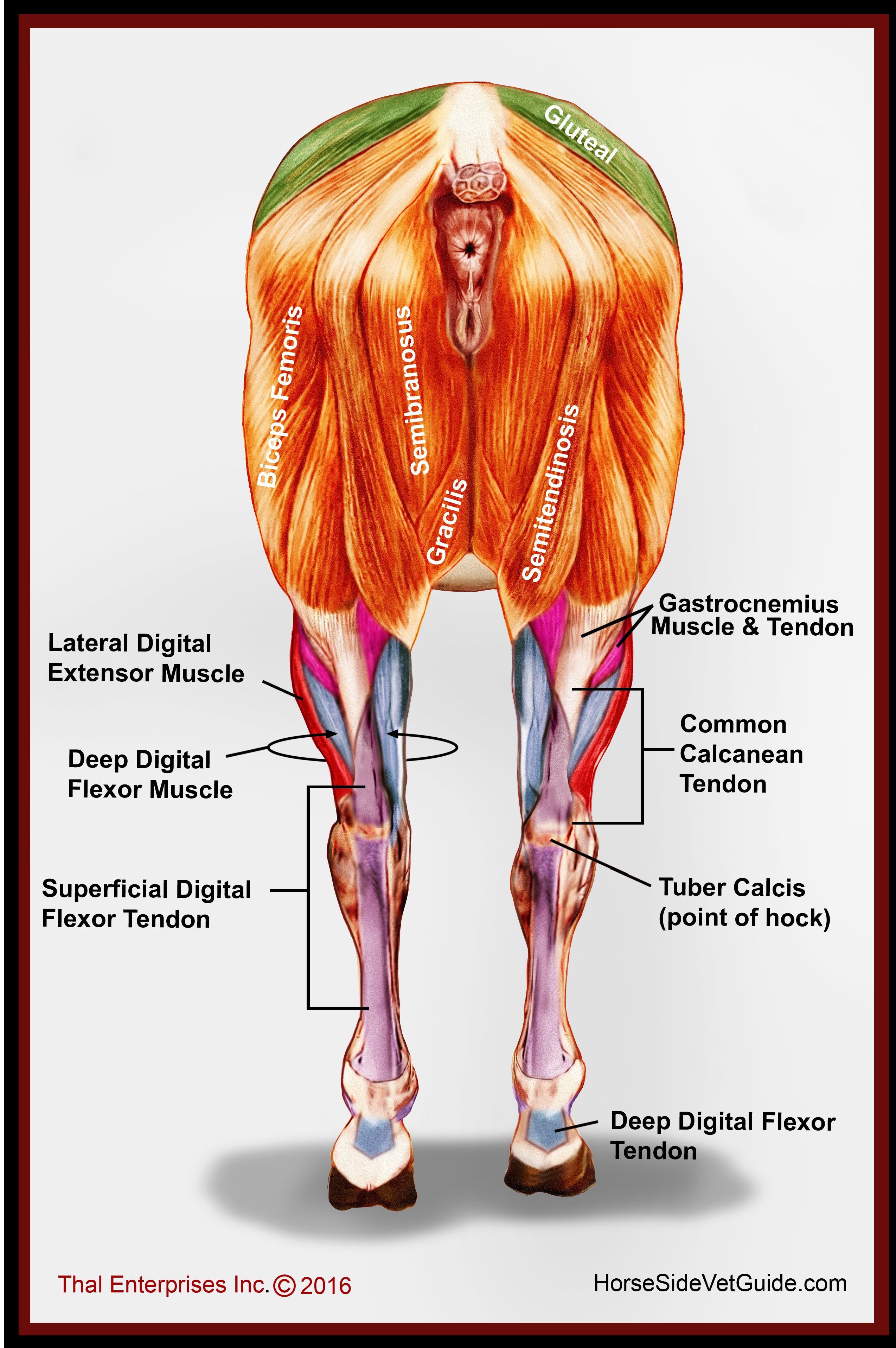
The hock joint is the largest joint on the horse's hind legs. The joint is made of several small bones, the most prominent being the Os Calsis which gives the hock its angular shape. The strength of the hocks is very important as this is the most active joint in the horse's hind legs. The equine hock is analogous to the human ankle.
Horse Legs Photograph by Carole Hinding
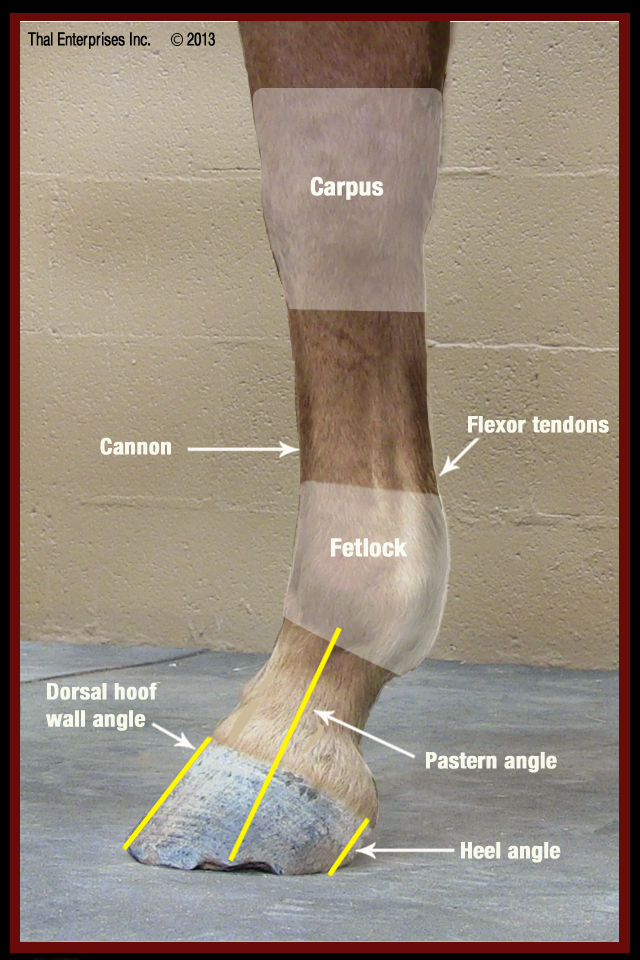
Since a horse's legs are made up of a finely tuned system of bones and joints, ligaments and tendons, muscles and connective tissue designed to carry a relatively heavy body, good conformation coupled with healthy limbs is extremely important for proper function. Important parts of the horse's forelimbs

hind legs of horse Stock Photo Alamy
The line leading from Eohippus to the modern horse exhibits the following evolutionary trends: increase in size, reduction in the number of hooves, loss of the footpads, lengthening of the legs, fusion of the independent bones of the lower legs, elongation of the muzzle, increase in the size and complexity of the brain, and development of crested, high-crowned teeth suited to grazing.

Quick Guide To Horse Leg Markings Horse markings, Horse care, Horses
Introduction The equine hind limb is also referred to as the pelvic hind limb. When working with horses, it is important to be able to accurately assess, diagnose and manage an equine patient. To do this, a good understanding of equine anatomy is essential. Anatomy

Legs of Horse in Movement. Close Up Stock Photo Image of movement, equine 42778144
The primary function of the front legs is to support most of the horse' s weight, absorb the shock of concussion, and lift the body for the flight phase of each stride. Strongest construction consists of relatively straight legs with sturdy bone structure, big flat knees, and well-shaped fetlock joints. Straightness

horse legs Archives LubriSynHA
Chestnut (horse anatomy) The chestnut, also known as a night eye, [1] is a callosity on the body of a horse or other equine, found on the inner side of the leg above the knee on the foreleg and, if present, below the hock on the hind leg. It is believed to be a vestigial toe, and along with the ergot form the three toes of some other extinct.

Leg Conformation The Horse
Because a horse's legs are made up of a finely tuned system of bones and joints, ligaments and tendons, muscles and connective tissue designed to carry a relatively heavy body, good body conformation combined with healthy limbs is extremely important for proper function.

Horse Health Helping your horse manage ringbone injury
Here is a list of some of the most common conformational defects seen in the limbs of horses: Toed in: One or both legs are rotated in towards one another. Toed out: One or both legs are rotated outwards away from each other. Tied In at the Knee: The cannon bone is narrower where it ties in with the knee joint.

Lameness, Severe, Cannot Support Weight on Limb Horse Side Vet Guide
Mammals Horse What's The Purpose of a Horse's Leg Chestnut? Advertisement Often called "night eyes," a horse's leg chestnut might seem unimportant now but it had a purpose years ago. Each one is unique, like a thumbprint, and grows continuously like fingernails.

Blood bay horse rearing on its hind legs Most Beautiful Horses, Pretty Horses, Horse Crazy
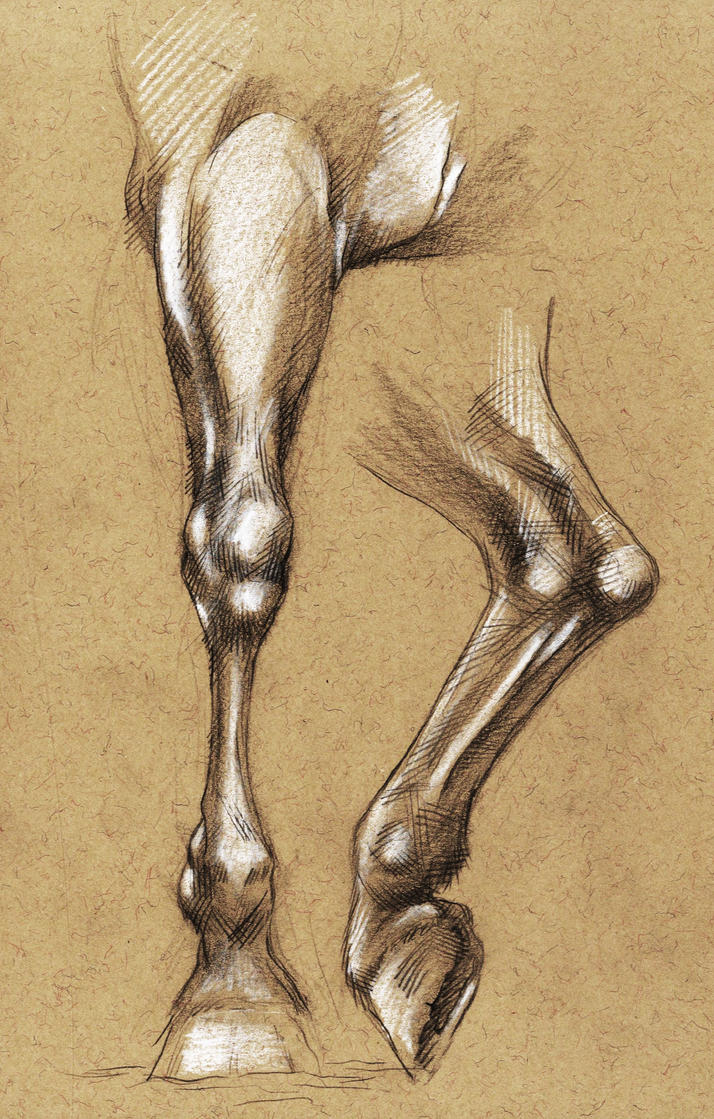
Parts of a horse on both the back and front legs. 32. Cannon bone and splint bone. The cannon bone is the large metacarpal below the knee (front) or the hock (back), and the splint bone is the small, bony pencil-like structure behind the cannon bone. These bones resemble the bones in our hands.
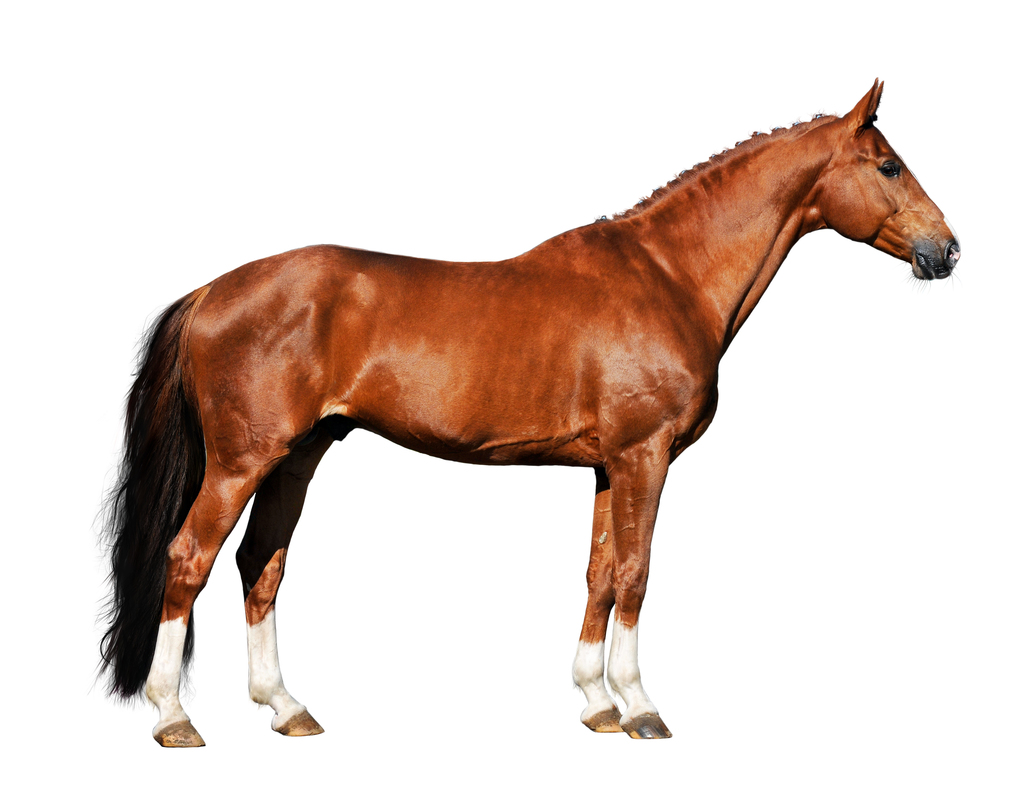

Horse Leg Anatomy Form and Function EquiMed Horse Health Matters
The horse leg anatomy in the rear includes the bones of the pelvis (the ilium, ischium, and pubic bones), femur, tibia, fibula, metatarsus, and phalanxes. It also includes the joints of the hip, stifles, hock, fetlock, pastern, and coffin. Hind limbs The top part of the hind limbs consists of three fused bones, called the ileum, ischium, and pubis.
/low-section-of-horse-515042659-58d91b435f9b58468381b5ac.jpg)
White Leg Markings on Horses
Tendons attach muscle to bone. When the muscle contracts force is applied to the bone through the tendon creating force which may be either static, as in the standing horse, or result in motion. Made of carefully arranged protein fibers, primarily collagen, tendons are elastic. As long as the elastic tendon is not over stretched it recovers to.
Horse leg anatomy by tirin54 on DeviantArt
In summary, horse legs are made up of various apparatuses consisting of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and connective tissue. All of these devices work together to help stand, move, and protect from injuries to the horse legs. Unfortunately, often horses face health problems like tendon or ligament injuries. Although there is a bunch of different.